Scratch
Scratch, a free resource developed at MIT, is arguably the most popular tool for introducing kids to coding, engaging millions of children worldwide. We consulted parents in large tech communities to evaluate Scratch's effectiveness and gather their pro tips for teaching kids to code with this platform. Whether you're a senior programmer or someone who has never written a line of code, you'll find valuable insights to kick off your child's Scratch coding adventures here. We'll also share some of the best books, online classes, and teaching methods to help kids learn Scratch.
A Quick Plug: If you're looking for a fun, educational Scratch social experience, consider joining our Saturday Scratch club, where young coders from Los Angeles to Brisbane, Australia gather weekly to build and share projects, facilitated by our amazing coding teacher. Modulo Members get 25% off and private lessons (you can join the community here).
Feel free to reach out if you’d like to try a free class before you commit.
1. What’s Scratch?
Scratch is a visual programming language and online community targeting users aged 8-16, developed by the Lifelong Kindergarten Group at the MIT Media Lab. It’s designed to teach programming concepts to people of all ages, especially children and beginners, in a fun and interactive way. No online access is required to use Scratch, making it more accessible than other programs. Parents can also disable online access to limit their children's interactions with the community.
2. Who is Scratch a fit for?
While Scratch was designed for users aged 8-16, many programmer parents believe it is ideally suited for children aged 6-9, from complete beginners to advanced coders. Younger children may want to use ScratchJr, designed for ages 5-7. Scratch works best for children who respond positively to its features and visual design, particularly highly self-directed learners.
3. Is Scratch an effective teaching tool?
Many families credit Scratch with nurturing a genuine passion for coding in their children. Passion for coding is crucial as it differentiates effective, innovative programmers from those whose work can be easily outsourced or automated. Great programmers are always learning and growing, driven by their passion.
Scratch has faced criticism for not being a well-structured coding language and lacking progressive learning. However, programmer parents overwhelmingly found Scratch to offer more educational benefits than drawbacks. Here are the main reasons why parents think Scratch is a great tool for teaching coding:
Self-paced Learning: Scratch allows kids to learn at their own pace, a critical component of effective mastery-based learning.
Encouragement: Kids see immediate results from their work and can share their projects with the online community, friends, and parents.
Understanding Coding Concepts: Scratch teaches kids to think like programmers, laying the foundation for understanding other concepts like loop control and embedded systems programming.
Skill Development: It encourages critical thinking, innovation, and problem-solving, applicable to various endeavors.
Exploration: Scratch encourages learning by doing and experimentation, allowing kids to tinker with other people’s projects.
Computational Thinking: It provides training in variables, loops, algorithms, and logic.
Inspiration to Advance: Scratch's limitations inspire kids to learn more advanced languages like Python to achieve their project goals.
4. Who is Scratch NOT a fit for?
While many children love Scratch, it’s not for everyone. The biggest challenge families cite is its exploratory nature, which may not suit children who need more structured, progressive learning. Families can combine Scratch with additional resources to provide more systematic learning.
Here’s who Scratch may not be the best choice for:
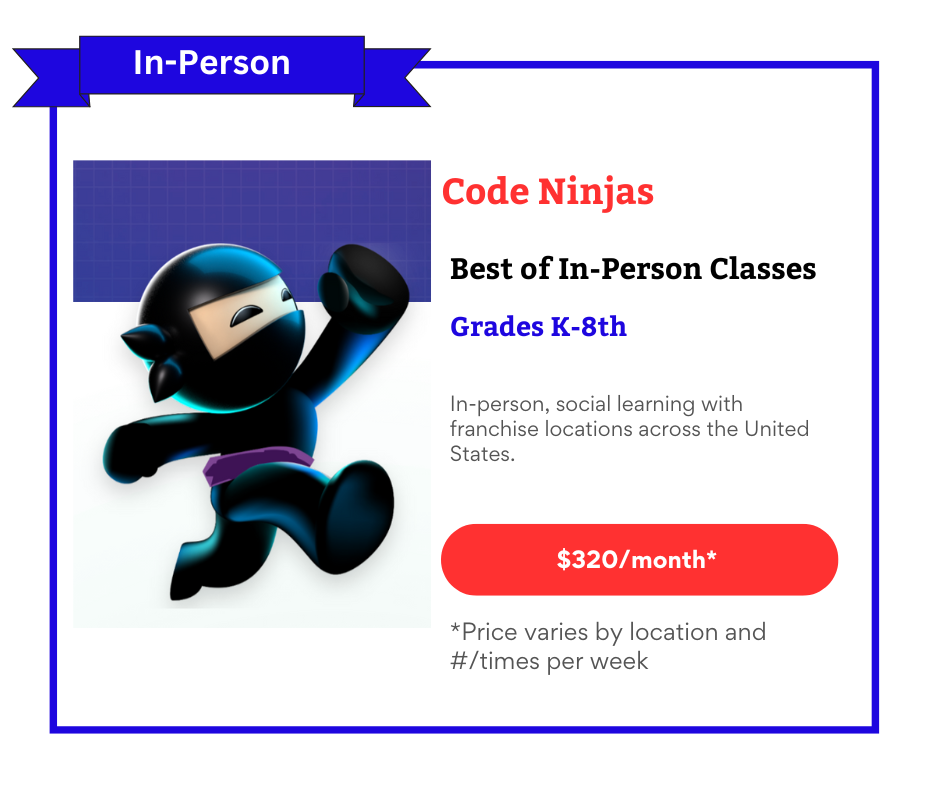
Kids Who Need More Structured Learning: Some kids thrive on structured, progressive learning. For these children, families might want to supplement Scratch with books, online tutorials, or formal classes. Other programs like code.org, Code Ninjas, or online classes at Udemy or Outschool might be more compelling.
Kids Who Don’t Like Scratch: Some children who enjoy coding may not resonate with Scratch. They might prefer introductory classes with languages like Python or JavaScript.
Kids Who Don’t Like Coding: Forcing a child to code if they don't enjoy it can be counterproductive. Coding can be beneficial for many careers, but it's not essential for all, and children may find other passions that are equally valuable.
Younger Children: For children under six or those finding Scratch too complex, ScratchJr is a more suitable option. ScratchJr introduces programming concepts in a simpler and more accessible way, with a companion book and 75 suggested activities.
5. Educational Value Score: 78/100
Scratch has received overwhelmingly positive reviews from homeschool parents. The key strengths highlighted include its unique and engaging approach to teaching coding, its accessibility, and its ability to foster creativity and critical thinking. The primary drawbacks mentioned are related to its lack of structured progression and occasional addictive tendencies
Uniqueness (10/10): Scratch stands out for its innovative use of visual blocks to teach coding, making it accessible and engaging for young learners. There are few comparable alternatives that offer such an intuitive and creative approach to programming (Cathy Duffy Reviews) (How to Homeschool).
Engagement (10/10): Parents and children find Scratch highly enjoyable. Its gamified approach and immediate feedback loop make it an exciting platform for kids to learn coding (How to Homeschool) (Homeschool.com).
Accuracy (9/10): Scratch provides accurate and reliable programming concepts. However, as it simplifies coding for young learners, some advanced accuracy in coding principles might be slightly compromised (Juni Learning) (Outschool).
User-Friendliness (10/10): The drag-and-drop interface of Scratch is extremely intuitive, even for young children and parents with no coding background. The platform is praised for its ease of navigation and minimal technical issues (How to Homeschool) (Juni Learning).
Pedagogy (9/10): Scratch is effective in teaching coding basics and computational thinking. It adapts well to different developmental stages, but some parents noted a need for more structured learning paths (Homeschool.com) (CodaKid).
Homeschooling (10/10): Homeschool parents highly recommend Scratch for its flexibility and suitability in a homeschooling environment. It provides ample resources for parents to integrate into their curriculum (How to Homeschool) (Homeschool.com).
Learning Focus (10/10): Scratch emphasizes deep, meaningful learning through project-based activities rather than test preparation, which aligns well with modern educational standards (Homeschool.com) (Outschool).
Personalization (9/10): Scratch allows customization of projects to suit individual learning needs, catering to a diverse range of learners (Juni Learning) (CodaKid).
Special Needs (9/10): The platform is accommodating for children with learning disabilities, providing a supportive environment for different learning paces and styles (CodaKid) (Outschool).
Value (10/10): Scratch is free, offering high educational benefits at no cost, which adds significant value for homeschool families (How to Homeschool) (Juni Learning).
Negative Criteria:
Boredom (1/10): Some children might find the exploratory nature of Scratch less engaging if they prefer more structured learning environments (Homeschool.com) (Outschool).
Addictive Components (3/10): While Scratch is highly engaging, there are concerns about its potential to become addictive, as children might spend excessive time on the platform (How to Homeschool) (CodaKid)
Violence (0/10): Scratch has no violent content, making it safe for young learners (Juni Learning) (Outschool).
Unhealthy Competition (1/10): The platform encourages sharing and collaboration rather than competition, though minor competitive elements in community projects are present (CodaKid) (Outschool).
Excessive Prioritization of School Standards (3/10): Scratch focuses on creativity and problem-solving rather than strictly adhering to school standards, which is generally positive but might not align with every educational requirement (Cathy Duffy Reviews) (CodaKid).
6. Pro Tips for Using Scratch
Scratch offers a versatile platform for learning coding skills. Here are a few pro tips from developer parents:
Consider ScratchJr for Younger or Inexperienced Learners: ScratchJr is a more accessible version designed for ages 5-7.
Start Simple, Progress to Complex: Encourage beginners to start with simple projects available in the "Ideas" tab or tutorials within Scratch.
Help Kids Follow Project Steps: Remind kids to follow project steps effectively to develop good programming practices.
Download and Modify Projects: Learning by modifying other users' projects can help kids understand how different elements work together and encourage experimentation.
Seek Mentorship and Guidance: Consider enrolling in tutoring programs or finding expert mentors for personalized learning.
Supplement with Additional Resources: Use books from the library, online tutorials, and platforms like Outschool for more structured learning.
7. Resources to Supplement Scratch
To enhance the Scratch experience, parents can supplement with tutorials, online classes, books, and tutors recommended by the tech community.
Online Tutorials: Scratch offers many tutorials on its website and YouTube channel. Popular tutorials include "How to Make a Jumping Game."
CS50 Introduction to Computer Science (Harvard University): Harvard’s introductory course covers Scratch in its first week.
Raspberry Pi: Offers multiple modules on Scratch.
Udemy Scratch Courses: Several highly acclaimed classes for Scratch and other languages.
Live Classes: Outschool offers many popular Scratch courses for all ages.
In-person Classes: Code Ninjas offers high-quality in-person coding classes worldwide.
Tutors: Expert mentors can nurture coding skills. Jippity combines AI with tutoring.
Books: Many books with Scratch lessons and project prompts are available at libraries. Some recommended books include:
Usborne Coding Games and Projects
"Coding Games in Scratch: A Step-by-Step Visual Guide to Building Your Own Computer Games"
"Super Scratch Programming Adventure! (Scratch 3)"
8. How to Get Started with Scratch
Visit the Scratch website (scratch.mit.edu) and sign up for a free account. The Scratch editor includes different sections:
Stage: Where programs run.
Sprites: Characters or objects that interact in programs.
Blocks Palette: Contains programming blocks to create scripts.
Kids can add characters, create scripts, save their projects, and share them with others. The best way to start is by exploring the vast Scratch community, discovering other projects, and learning from tutorials and resources shared by users.
The Scratch YouTube channel also has many tutorials on every aspect of Scratch.
9. After Scratch
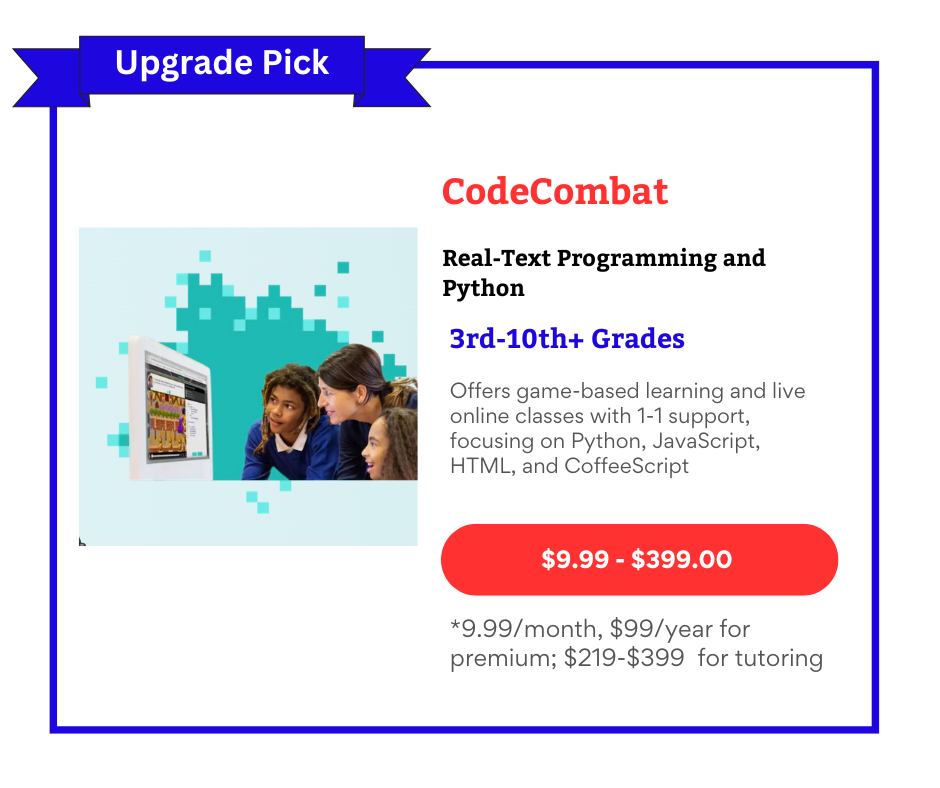
Scratch is particularly beneficial for children aged 6-8, providing a strong foundation in programming concepts. As they advance, children can explore more complex programming languages like Python, C#, and Ruby. Platforms like Udemy and Outschool offer great coding classes. For game development, CodeCombat and Unity provide seamless progression from Scratch to creating more complex programs.
Thanks to all the developer parents who weighed in on my questions!
Reddit: Discussions on coding for kids.
Hacker News: Teaching kids to code and the effectiveness of Scratch.










The Raspberry Pi, developed by Eben Upton and his team at the University of Cambridge, was created to address declining interest in computer science among students. Designed as an affordable, programmable computer, it aims to make computing accessible to all. Celebrated for its affordability, versatility, and active global community, the Raspberry Pi is widely used in education, industry, and hobbyist projects. It’s ideal for homeschooling, offering structured learning in programming, hardware interaction, and problem-solving through hands-on projects. With a broad age range suitability and cost-effective options, the Raspberry Pi provides an engaging and impactful STEM education tool, despite a learning curve for beginners.